Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that acts as both excitatory and inhibitory. It is often regarded as the reward hormone however it is responsible for many actions in the body including motivation, mood, learning, memory, pleasure, sleep and movement.
People who have low dopamine levels present with symptoms such as:
- addictive tendencies
- lack of motivation/satisfaction
- lack of energy/drive
- low libido
- mood swings
- obsessive-compulsive disorders
- depression
- unable to concentrate.
- inability to lose weight
One of the common presentations of low dopamine is the addictive tendencies including alcohol, caffeine, sugar, smoking as well as modern addictions such as texting, shopping, scrolling, video games, power and money. People reach for these ‘addictions’ in order to give them a dopamine boost. In summary dopamine is responsible for giving you that zest for life.
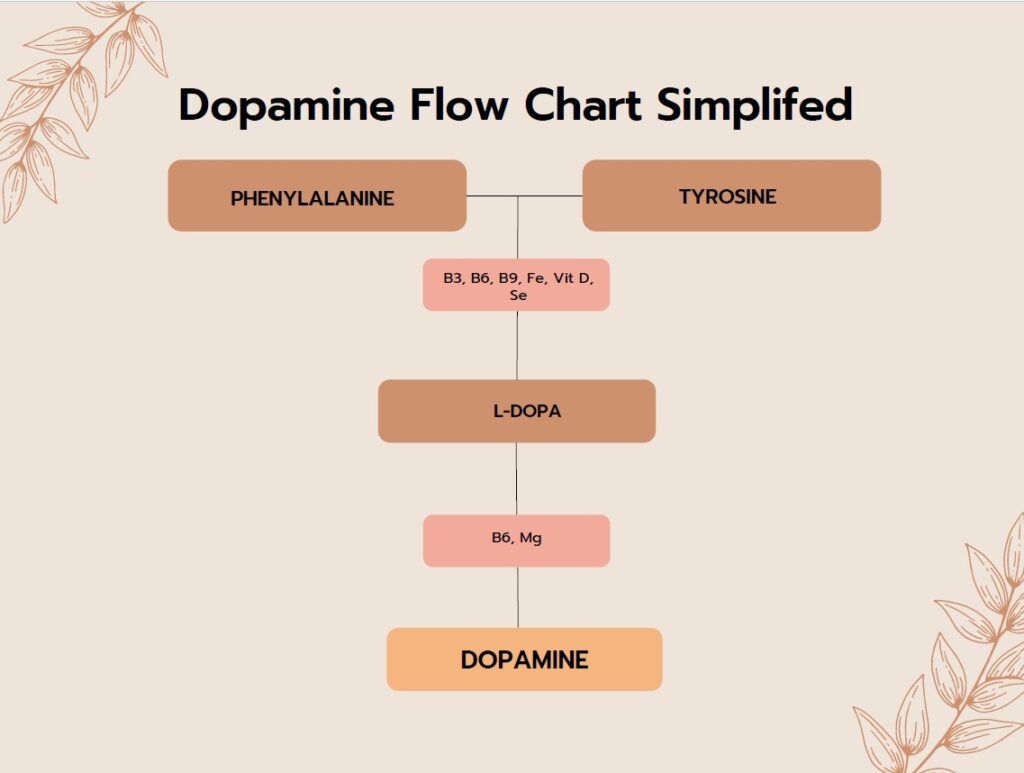
The chart is a summarised version of the conversion and production of dopamine in the body. Phenylalanine and tyrosine are the major amino acids that together form dopamine. In order for these amino acids to produce dopamine there are many nutritional cofactors that must be present for this conversion to occur including B vitamins, iron, magnesium, vitamin D, selenium. One of the many reasons people experience low dopamine levels is due to poor nutrition prohibiting this conversion.
Furthermore, dopamine continues to be processed further. There are many genetic factors which can cause people to process dopamine faster or slower than usual and again nutrition is a key component to this, ensuring that the cofactors required for dopamine to be processed. People who have issues with their dopamine levels may also benefit from herbal medicines which have the ability to impact these pathways.
